After the revolutionary AI chat system ChatGPT, OpenAI, the artificial intelligence company founded by Elon Musk, has recently released a new tool called Point-E, which can generate 3D images of objects based on text.
This technology is a major step forward in AI generators, as it allows for creating 3D models in a matter of seconds without needing costly optimization.
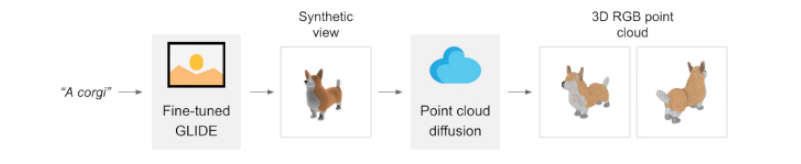
Point-E generates a synthetic 3D rendering of the object in question and then runs that image through a series of models to create a 3D-coloured point cloud. While the resulting images may not be as detailed or original as some AI image generators, Point-E has the advantage of being much faster than its competitors.
The 3D imaging industry is one of the largest and most diverse, with applications in fields ranging from construction and architectural design to film and television production and video game development. Point-E has the potential to revolutionize the way 3D models are created and used, making the process faster and more efficient.
One of the key advantages of Point-E is its resource efficiency. Unlike other AI image generators like Google’s DreamFusion, Point-E can produce results in a much shorter time frame, making it an attractive option for those looking to quickly generate 3D models.
Point-E is based on other more traditional 2D image generators like DALL-E 2 and Craiyon (formerly known as DALL-E mini) and uses a smaller data set of pairs to create the point cloud that will shape the geometry of the 3D object. The source code for Point-E is available on Github, allowing anyone to try the technology themselves.
Overall, Point-E represents an exciting step forward in the field of AI image generation and has the potential to significantly impact the 3D imaging industry. Point-E’s effectiveness and speed make it a potential tool for the future, even if the technology is still in its early stages and the images produced may not be as detailed as those produced by some other AI generators.
